THE SCIENCE OF GLYMPHATIC FLOW
When the world goes quiet and consciousness fades, your brain begins its most essential nightly task — self-cleaning. Electrical chatter slows, interstitial spaces widen, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pushes through tiny perivascular tunnels to wash away the day’s debris: misfolded proteins, oxidized lipids, and neurochemical static.
This hidden hydraulic network, discovered barely a decade ago, is known as the glymphatic system — the brain’s own detox circuit. Its significance cannot be overstated. When it works, neurons reset. When it falters, toxins accumulate, thought becomes heavy, and the spark of creativity dulls.
The Hidden Plumbing of the Brain
In 2012, Dr. Maiken Nedergaard’s team at the University of Rochester mapped this system for the first time [1]. They found that astrocytes — glial cells once thought to be mere support tissue — form a perivascular network that channels CSF deep into the brain. Through aquaporin-4 (AQP4) water channels, fluid mixes with the interstitial space, collecting metabolic waste such as β-amyloid, tau proteins, and excess ions before draining out through venous and lymphatic pathways [2–3].
During slow-wave sleep, when neural firing synchronizes into rhythmic delta oscillations, interstitial spaces expand by up to 60 percent [4]. Fluid rushes through like a tide, clearing waste at speeds impossible during waking hours. Deep sleep, in other words, is not rest — it’s repair.
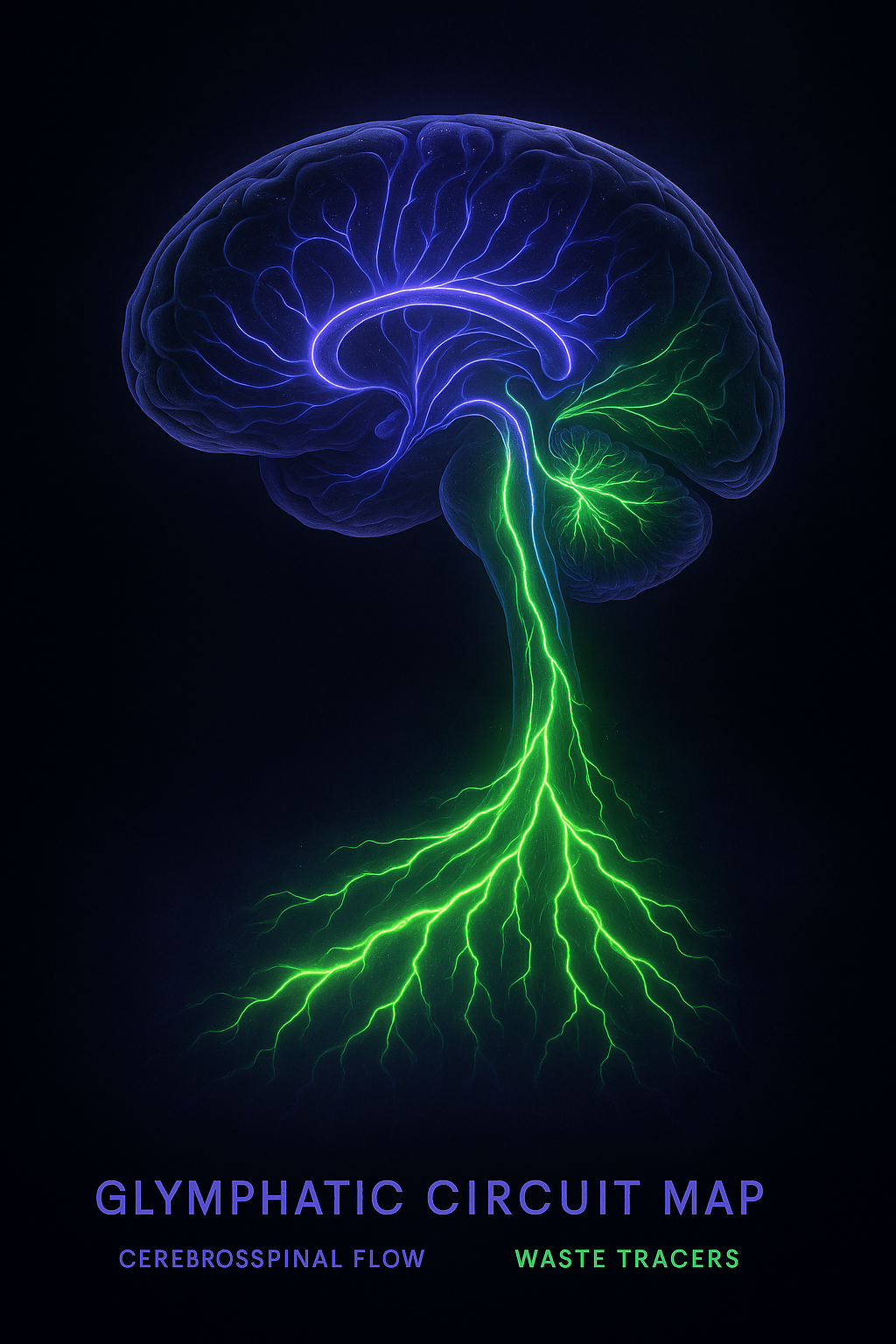
Circadian Timing and Hormonal Cross-Talk
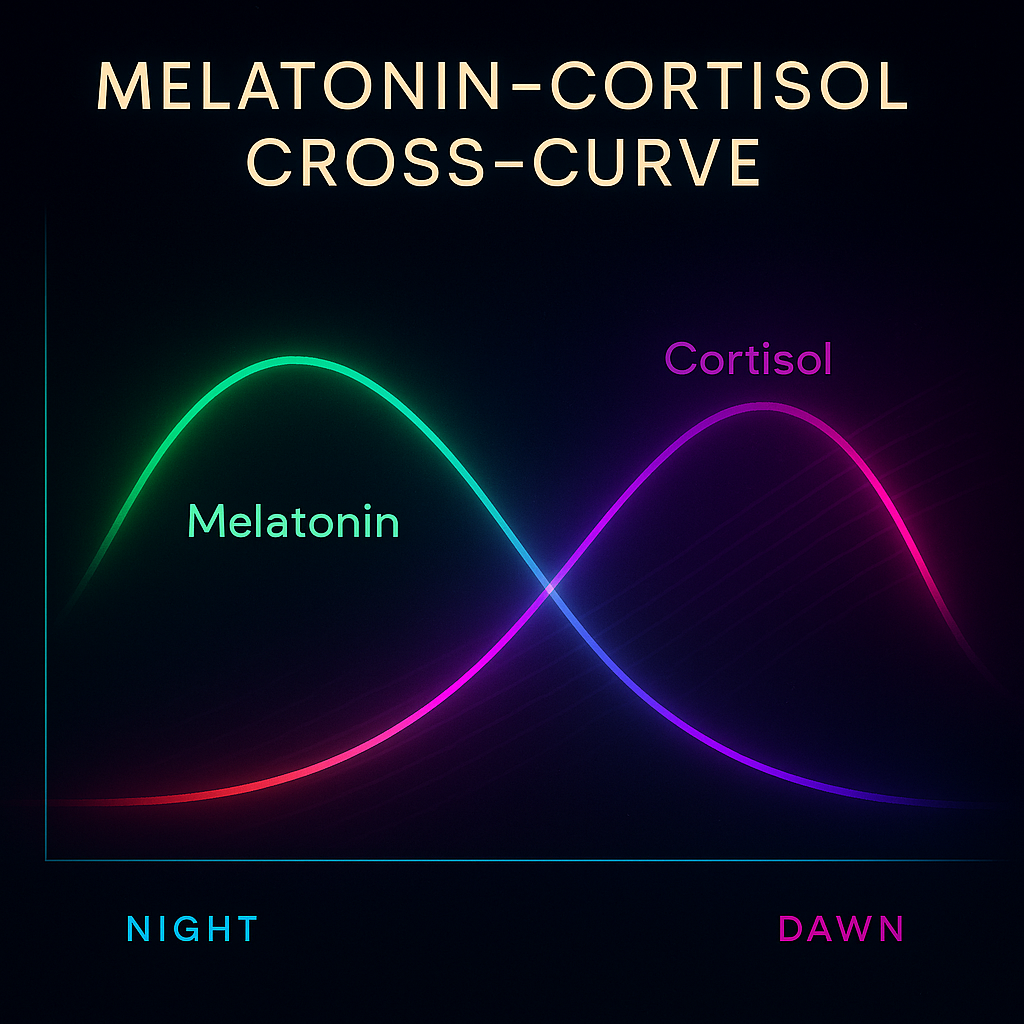
The body’s circadian clock regulates the glymphatic system. Melatonin, released from the pineal gland after darkness, dilates blood vessels and amplifies CSF pulsation [5]. Cortisol, in contrast, rises in the morning, tightening vascular tone and signalling wakefulness. When this rhythm is reversed — by late-night light exposure or chronic stress — the system loses its nightly drive.
Research shows that AQP4 gene expression follows a circadian rhythm. Blue-light exposure after 10 p.m. suppresses melatonin, blunting AQP4 activity and glymphatic efficiency [6]. This underscores the fact that our lifestyle choices, such as late-night light exposure, aren’t just cosmetic biohacks — they’re molecular triggers for drainage, and we have the power to control them.
Affiliate suggestions: Swanwick Blue Light Glasses, Bon Charge Red Night Lamps, or Somnifix mouth strips for nasal breathing reinforcement.
When Flow Fails
When this nightly rinse stagnates, damage accumulates. Poor sleep accelerates β-amyloid plaque buildup — the pathology seen in Alzheimer’s [8–9]. Chronic sleep debt increases oxidative stress, disrupts dopamine signalling, and slows cognitive processing. These are serious consequences that should motivate us to prioritize our sleep.
Neural congestion, as we term it at Cortex Cannibal, is a state where the mind’s electrical circuitry is overwhelmed by the accumulation of metabolic waste, a condition that can be detrimental to brain health.
Inflammation, Endothelial Health & Brain Drain
The glymphatic system is powered by arterial pulsation. When endothelial health declines — due to inflammation, high cortisol levels, or nitric oxide depletion — the pumping action weakens. Vessels stiffen, pressure waves flatten, and CSF flow slows.
Systemic inflammation (from processed diets, sleep deprivation, or gut dysbiosis) constricts microvessels and collapses the perivascular space. Restoring nitric oxide production through cold exposure, nasal breathing, and nitrate-rich foods improves vascular elasticity [11–12].
As a tie-in ritual, we recommend an alternate hot-cold shower or ice face immersion, which can activate the parasympathetic nervous system and promote vasodilation rebound, thereby enhancing the glymphatic system’s function.
Tie-in affiliate: HumanN SuperBeets, Cymbiotika Nitric Oxide Drops, Elemental Cold Plunge setups.
Interconnected Pathways
The glymphatic system merges with meningeal lymphatic vessels that drain into the neck’s cervical nodes [13]. Posture, jaw tension, and breathing directly affect outflow. Humming, tongue posture, and diaphragmatic nasal breathing enhance nitric-oxide flow and lymphatic motion [14]. Even gentle neck mobility exercises before bed increase drainage efficiency.
Momentous Magnesium Threonate → deepens slow-wave density
- Momentous Magnesium Threonate → deepens slow-wave density
- Double Wood Apigenin → GABA-modulated calm
- Thorne Super EPA → astrocyte membrane support
- Bon Charge Blue-Light Glasses → circadian protection
- Cymbiotika Nitric Oxide → vascular elasticity and brain oxygenation
(Educational only — affiliate links disclosed for transparency. Not medical advice.)
THE RITUAL, RECOVERY, AND OPTIMIZATION
The Environment
- Temperature: Set your space around 18°C / 65°F. Cooler air promotes the release of melatonin and increases parasympathetic tone.
- Darkness: Eliminate every light source. Even small LED glows suppress melatonin.
- Silence or a steady, low-frequency hum: This removes limbic threat monitoring and deepens delta oscillations.

The Breath Circuit
- Practice 4-second nasal inhalations and 6-second exhalations for ten minutes before bed.
- Avoid mouth breathing entirely — it collapses nitric oxide signalling.
- Optional: Somnifix mouth strips to train nasal dominance.
Breathing isn’t just relaxation. It’s the mechanical driver of CSF pulsation. Each diaphragmatic contraction creates pressure gradients that push cerebrospinal fluid through perivascular spaces.
The Advanced Sleep Stack
- Magnesium L-Threonate — boosts slow-wave amplitude and synaptic plasticity.
- Apigenin (Chamomile Extract) — extends total sleep time and reduces latency.
- L-Theanine — smooths alpha-to-theta transitions for effortless descent into SWS.
- Glycine (3 g) — lowers core temperature and supports REM onset.
- Tart Cherry Extract — natural melatonin source with anti-inflammatory polyphenols.
- Ashwagandha or Reishi — adaptogenic support for cortisol modulation.
Combine these for a neural-reset stack. Pair with herbal teas rich in apigenin and L-theanine (e.g., chamomile, green tea, lemon balm).
Affiliate suggestions: Momentous Magtein, NOW Glycine, Thorne Tart Cherry, Cymbiotika Reishi Elixir.
Nutrition for Nocturnal Clearance
Dinner timing affects brain detox. Eating within two hours of sleep diverts blood flow away from digestion, thereby limiting CSF pressure waves.
Aim for last meal 3–4 hours before bed, focusing on:
- Omega-3-rich fish
- Complex carbs like sweet potato (tryptophan carrier)
- Dark leafy greens (magnesium source)
- Fermented foods for gut–brain signalling
Internal link: Cortex Cannibal Fermented Foods & Brain Health Blog
Internal link: Mitochondria & Brain Energy Blog
The Cold Interface
A cold rinse before bed (or even facial immersion in cold water) resets vagal tone. It triggers the release of nitric oxide, thereby preparing the vascular network for nighttime blood flow.
This step pairs perfectly with the Nitric Oxide & Brain Power blog protocol — the morning contrast to the night’s detox ritual.

Posture and Drainage
- Side sleeping (preferably on the right side) enhances interstitial clearance by up to 25% compared to the supine position [15].
- Avoid stacked pillows that kink cervical drainage.
- Gentle neck stretches before bed facilitate lymphatic movement into the subclavian veins.

The Cortex Cannibal Sleep Ritual (Summary Map)
Step 1: Screen blackout for 90 minutes before bed.
Step 2: Magnesium + apigenin stack.
Step 3: Breathwork sequence.
Step 4: Cold rinse → darkness → side sleep.
Step 5: Wake naturally, then hydrate and expose your eyes to early sunlight to reset your circadian phase.
CTA: Download the free Cortex Cannibal “Sleep & Glymphatic Flow Cheat Sheet.”
The Takeaway
Glymphatic flow isn’t a luxury — it’s maintenance. Each night, cerebrospinal tides cleanse the circuits that define who you are.
Protect that cycle like oxygen: align your light, temperature, posture, and chemistry.
This is where neuroscience meets ritual — the convergence of biology and discipline that fuels every Cortex Cannibal transformation.
Devour the brain before it devours you.
References —
Nedergaard M. et al. Science Translational Medicine. 2012 — Discovery of the glymphatic system and its cerebrospinal fluid transport network.
Iliff J.J. et al. Journal of Neuroscience. 2013 — Cerebral arterial pulsation drives perivascular CSF–interstitial fluid exchange.
Xie L. et al. Science. 2013 — Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain.
Rasmussen M.K. et al. Nature Neuroscience. 2018 — Dynamic regulation of brain interstitial fluid during sleep.
Shokri-Kojori E. et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA). 2018 — β-Amyloid accumulation after one night of sleep deprivation.
Tosini G., Ferguson I., Tsubota K. Progress in Brain Research. 2021 — Effects of blue light on circadian rhythms and melatonin suppression.
Fultz N.E. et al. Science. 2019 — Coupled electrophysiological, hemodynamic, and CSF oscillations in human sleep.
Yang L. et al. Nature Communications. 2013 — Glymphatic dysfunction accelerates amyloid deposition.
Tarasoff-Conway J.M. et al. Nature Reviews Neurology. 2015 — Clearance systems of the brain and implications for Alzheimer’s disease.
Benveniste H. et al. Neurochemical Research. 2019 — Mechanisms of glymphatic transport and sleep impairment.
Dreha-Kulaczewski S. et al. Journal of Neuroscience. 2015 — Inspiration-driven movement of CSF and its synchronization with respiration.
Larsen F.J. et al. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2014 — Nitrate supplementation and nitric-oxide-mediated vascular function.
Louveau A. et al. Nature. 2015 — Discovery of meningeal lymphatic vessels linking the brain and immune system.
Lundberg J.O. et al. European Respiratory Journal. 2011 — Nasal nitric oxide and upper-airway physiology.
Lee H. et al. Journal of Neuroscience. 2015 — Lateral (side) sleeping position enhances glymphatic transport.
O’Donnell J. et al. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2021 — Sleep, circadian rhythms, and glymphatic system interactions.
Saper C.B., Scammell T.E., Lu J. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2022 — Neural regulation of sleep–wake states and homeostatic maintenance.
Bazinet R.P., Layé S. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2020 — Role of omega-3 fatty acids in astrocyte and neuronal membrane function.
Slutsky I. et al. Neuron. 2010 — Magnesium-L-threonate and synaptic density modulation.
Nathan P.J. et al. Biological Psychology. 2006 — L-Theanine and alpha-wave modulation during relaxation.
